Employment and taxes everfi quiz answers – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of employment and taxes with our exclusive EverFi quiz answers guide. This in-depth resource unravels the complexities of employment taxes, empowering you with a thorough understanding of your rights, obligations, and the intricate tax landscape.
From understanding the different types of employment taxes and their calculation to navigating employer responsibilities and employee rights, our guide provides a roadmap through the intricacies of employment taxation. Discover the significance of tax exemptions and deductions, delve into the intricacies of tax forms and reporting, and gain invaluable insights into the consequences of non-compliance.
Understanding Employment Taxes: Employment And Taxes Everfi Quiz Answers

Employment taxes are a significant component of the tax system in the United States. They are levied on employers and employees to fund various government programs, including Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance.
There are three main types of employment taxes: Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA), Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA), and State Unemployment Tax Act (SUTA).
FICA taxes are withheld from employee paychecks and include Social Security and Medicare taxes. Social Security taxes are used to fund retirement and disability benefits, while Medicare taxes fund healthcare for the elderly and disabled.
FUTA and SUTA taxes are paid by employers and are used to fund unemployment insurance programs. FUTA taxes are paid to the federal government, while SUTA taxes are paid to state governments.
The amount of employment taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck is based on their gross wages and the applicable tax rates. Employers are responsible for withholding the correct amount of taxes and remitting them to the appropriate tax authorities.
Employer Responsibilities

Employers have several legal obligations regarding employment taxes, including:
- Registering with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and state tax authorities for employment tax purposes
- Withholding the correct amount of employment taxes from employee paychecks
- Remitting employment taxes to the appropriate tax authorities
- Filing employment tax returns on a regular basis
Employers must also provide employees with a Form W-2, which shows the amount of wages earned and taxes withheld during the year.
Employee Rights and Obligations
Employees have certain rights and obligations related to employment taxes, including:
- The right to receive a Form W-2 from their employer
- The obligation to report all of their income to the IRS, including wages and self-employment income
- The obligation to pay their share of employment taxes
Employees who fail to comply with employment tax laws may be subject to penalties and interest charges.
Tax Exemptions and Deductions
There are a number of tax exemptions and deductions available to employees that can reduce the amount of employment taxes they owe.
- Exemptions:Exemptions are based on personal circumstances, such as marital status and number of dependents. They reduce the amount of income that is subject to taxation.
- Deductions:Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from gross income before taxes are calculated. Common deductions include contributions to retirement accounts, health insurance premiums, and mortgage interest.
Employees can claim exemptions and deductions on their tax returns.
Tax Forms and Reporting
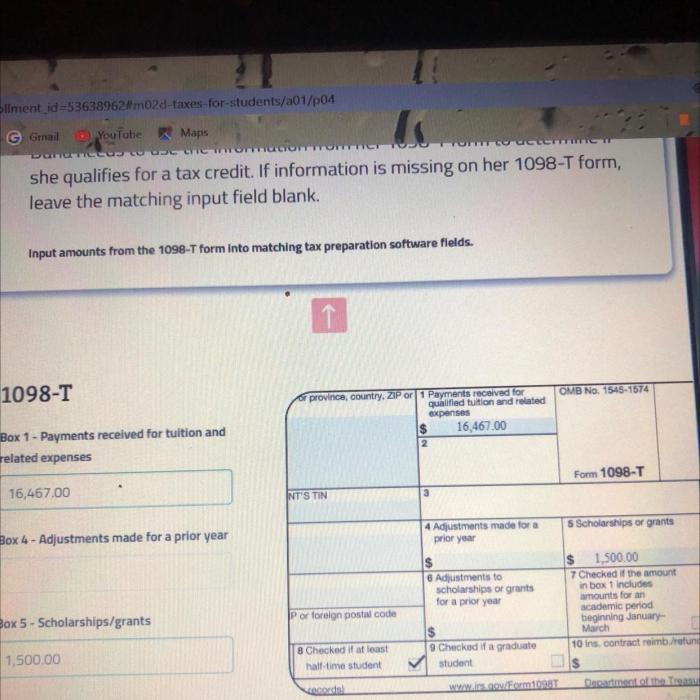
Employers and employees use a variety of tax forms to report employment taxes, including:
- Form W-2:Issued by employers to employees, shows wages earned and taxes withheld during the year
- Form 941:Filed by employers quarterly, reports FICA taxes withheld from employee paychecks
- Form 940:Filed by employers annually, reports FUTA taxes paid
- Form 1040:Filed by employees annually, reports income and taxes owed
It is important to complete and file tax forms accurately and on time to avoid penalties and interest charges.
FAQ Compilation
What are the different types of employment taxes?
Employment taxes encompass FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act), FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act), and SUTA (State Unemployment Tax Act).
How are employment taxes calculated and withheld?
Employment taxes are calculated based on employee wages and withheld directly from paychecks.
What are the responsibilities of employers regarding employment taxes?
Employers are legally obligated to collect, withhold, and remit employment taxes to the appropriate tax authorities.
What rights do employees have related to employment taxes?
Employees have the right to receive accurate information about employment taxes and to file for tax exemptions and deductions.
What are the consequences of failing to comply with employment tax laws?
Non-compliance with employment tax laws can result in penalties, fines, and even criminal charges.