Lifespan development a psychological perspective second edition – In Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective, Second Edition, the authors provide a comprehensive overview of the field of lifespan development, from infancy to old age. The book covers a wide range of topics, including physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and personality development.
It also discusses the ways in which lifespan development is influenced by the social and cultural context in which it occurs.
This book is an essential resource for anyone interested in understanding human development across the lifespan. It is written in a clear and concise style, and it is packed with up-to-date research findings. The authors do an excellent job of integrating theory and research, and they provide a balanced perspective on the field of lifespan development.
Introduction
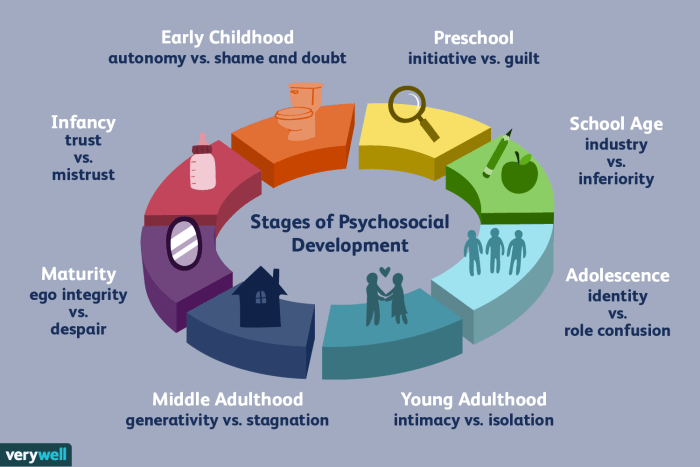
Lifespan development is the study of human development from conception to death. It is a multidisciplinary field that draws on insights from psychology, sociology, anthropology, and other disciplines. Lifespan development researchers are interested in understanding how people change over time, and how these changes are influenced by biological, cognitive, social, and cultural factors.
The book “Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective, Second Edition” provides a comprehensive overview of the field of lifespan development. The book is divided into nine chapters, each of which covers a different aspect of development. The chapters are written by leading experts in the field, and they provide a state-of-the-art review of the research on lifespan development.
Theoretical Perspectives on Lifespan Development
There are a number of different theoretical perspectives on lifespan development. These perspectives can be divided into three broad categories: biological, cognitive, and sociocultural.
Biological Theories
Biological theories of lifespan development focus on the role of genes and other biological factors in development. These theories argue that our genes play a major role in shaping our physical and psychological development. They also argue that our environment can influence our development, but that these influences are mediated by our genes.
Cognitive Theories, Lifespan development a psychological perspective second edition
Cognitive theories of lifespan development focus on the role of cognition in development. These theories argue that our thoughts and beliefs about ourselves and the world around us play a major role in shaping our development. They also argue that our cognitive development is influenced by our experiences, but that these experiences are interpreted through the lens of our existing beliefs and knowledge.
Sociocultural Theories
Sociocultural theories of lifespan development focus on the role of social and cultural factors in development. These theories argue that our development is shaped by the social and cultural context in which we live. They also argue that our social and cultural experiences can influence our thoughts and beliefs about ourselves and the world around us.
Methods in Lifespan Development Research

There are a number of different research methods that can be used to study lifespan development. These methods can be divided into three broad categories: longitudinal, cross-sectional, and mixed-methods approaches.
Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies follow the same group of people over time. This type of study can provide valuable insights into how people change over time. However, longitudinal studies can be expensive and time-consuming to conduct.
Cross-sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies compare people of different ages at a single point in time. This type of study can provide a snapshot of how people change over time. However, cross-sectional studies cannot provide information about how individuals change over time.
Mixed-Methods Approaches
Mixed-methods approaches combine longitudinal and cross-sectional methods. This type of study can provide a more comprehensive understanding of how people change over time. However, mixed-methods studies can be complex and challenging to conduct.
Physical Development

Physical development refers to the changes in a person’s body and physical abilities that occur throughout the lifespan. These changes are influenced by a number of factors, including genetics, nutrition, and environment.
Prenatal Development
Prenatal development begins at conception and ends at birth. During this period, the fetus grows from a single cell into a fully formed human being. The fetus is particularly vulnerable to environmental influences during this period, and exposure to toxins or other harmful substances can have a negative impact on development.
Infancy
Infancy begins at birth and ends at about 18 months. During this period, infants grow rapidly and develop a number of new physical abilities, such as walking and talking. Infants are also highly dependent on their caregivers for survival.
Childhood
Childhood begins at about 18 months and ends at about 12 years. During this period, children continue to grow and develop physically. They also develop a number of new cognitive and social skills. Children are increasingly independent during this period, but they still need the support and guidance of their caregivers.
Adolescence
Adolescence begins at about 12 years and ends at about 18 years. During this period, teenagers experience a number of physical changes, including a growth spurt and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Teenagers also develop a number of new cognitive and social skills.
They become more independent and begin to form their own identities.
Young Adulthood
Young adulthood begins at about 18 years and ends at about 40 years. During this period, young adults reach their physical peak. They are also likely to finish their education and begin their careers. Young adults are increasingly independent and make their own decisions about their lives.
Middle Adulthood
Middle adulthood begins at about 40 years and ends at about 65 years. During this period, adults begin to experience some physical decline. They may also experience changes in their career and family life. Middle adults are likely to be more reflective about their lives and to focus on their relationships with others.
Late Adulthood
Late adulthood begins at about 65 years and ends at death. During this period, adults experience significant physical decline. They may also experience cognitive decline and need assistance with daily activities. Late adults are likely to focus on their health and well-being and to spend time with their loved ones.
Answers to Common Questions: Lifespan Development A Psychological Perspective Second Edition
What is lifespan development?
Lifespan development is the study of human development across the entire lifespan, from conception to death. It is a multidisciplinary field that draws on insights from psychology, sociology, anthropology, and other disciplines.
What are the key concepts in lifespan development?
Some of the key concepts in lifespan development include:
- Development is a lifelong process.
- Development is multidimensional.
- Development is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and culture.
- Development is not always linear.
What are the major theoretical perspectives on lifespan development?
There are a number of major theoretical perspectives on lifespan development, including:
- Biological theories
- Cognitive theories
- Sociocultural theories
