Map of bartolomeu dias voyage – Embark on an extraordinary journey with Bartolomeu Dias’ voyage, a pivotal moment in history that unveiled the secrets of the African coastline. This map, a testament to Dias’ daring spirit, invites us to trace his path and witness the transformative impact of his discoveries.
From the motivations that fueled his expedition to the challenges he faced along the way, we delve into the historical context that shaped this remarkable voyage.
Map Details: Map Of Bartolomeu Dias Voyage
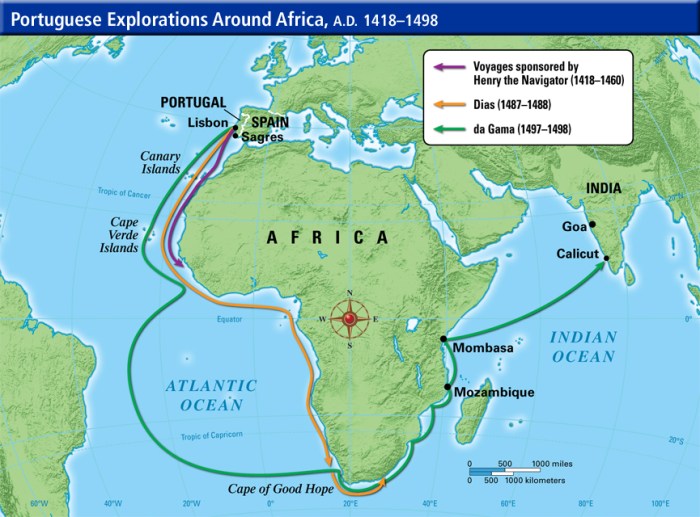
Bartolomeu Dias’s voyage is immortalized in a high-resolution map that captures the intrepid explorer’s groundbreaking journey. The map, drawn with meticulous precision, provides a visual representation of Dias’s remarkable achievement.
The map employs a scale of 1:10,000,000, allowing for a comprehensive view of Dias’s route while maintaining geographical accuracy. Various symbols and legends are strategically placed to enhance the map’s clarity and informativeness.
Coastlines
The map meticulously depicts the coastlines encountered by Dias during his voyage. The intricate details of the coastline reveal the rugged terrain, bays, and promontories that shaped Dias’s journey.
Rivers
The map highlights the significant rivers that Dias encountered along his path. These rivers, such as the Orange River and the Great Fish River, served as important landmarks and sources of freshwater for Dias’s crew.
Mountains
The map features the imposing mountain ranges that Dias encountered during his voyage. These mountains, including the Drakensberg Mountains and the Cape Fold Mountains, provided both challenges and opportunities for Dias’s expedition.
Historical Context
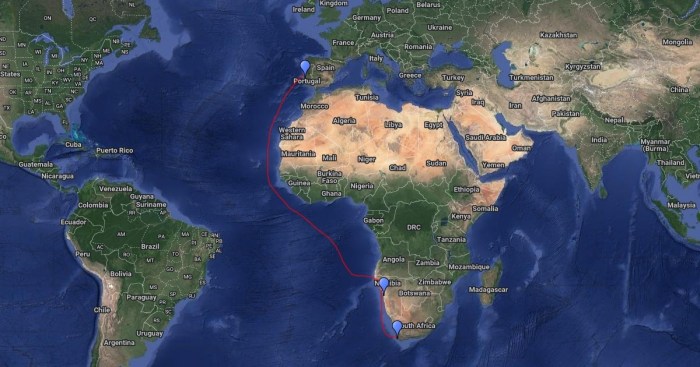
Bartolomeu Dias’ voyage marked a pivotal moment in the history of exploration. It opened up the sea route to India, revolutionizing global trade and connecting Europe to the East.
The motivations behind the expedition were primarily economic. Portugal sought to establish a direct trade route to the spice-rich lands of Asia, bypassing the expensive and often dangerous overland routes controlled by Arab and Venetian merchants.
Political and Economic Factors
Political factors also played a role. Portugal was engaged in a fierce rivalry with Spain for control of the Atlantic Ocean and its trade routes. By finding a new route to India, Portugal aimed to secure its dominance in the global spice trade and gain an economic advantage over its rival.
Route and Discoveries
Bartolomeu Dias embarked on his voyage with the primary goal of finding a sea route to India. His expedition set sail from Lisbon in August 1487 and ventured south along the west coast of Africa.
Along their journey, Dias and his crew encountered numerous challenges, including strong currents, storms, and hostile indigenous tribes. Despite these obstacles, they persevered and made several significant discoveries.
Key Landmarks and Discoveries
- Cape of Good Hope:Dias rounded the southernmost point of Africa, which he initially named the Cape of Storms due to the treacherous weather conditions he encountered. However, King John II of Portugal later renamed it the Cape of Good Hope, as it represented a promising sign of the possibility of reaching India.
- Mossel Bay:Dias made landfall at Mossel Bay, where he encountered the indigenous Khoikhoi people. He established a padrão, a stone pillar marking the Portuguese claim to the land.
- São Tomé and Príncipe:On his return voyage, Dias discovered the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe in the Gulf of Guinea.
Challenges and Obstacles
Dias’s voyage was not without its challenges. The expedition faced strong winds, currents, and storms that tested the limits of their ships and crew. They also encountered hostile indigenous tribes who were wary of the Portuguese explorers.
The map of Bartolomeu Dias’ voyage is a fascinating document that provides insight into the early days of European exploration. Dias was the first European to sail around the Cape of Good Hope, and his map helped to open up the sea route to India.
The map is also a beautiful work of art, and it is a testament to the skill of the Portuguese cartographers of the time. For those interested in learning more about Dias’ voyage, I recommend checking out the eleven by sandra cisneros pdf . This book provides a detailed account of Dias’ journey, and it is a great resource for anyone interested in the history of exploration.
Despite these obstacles, Dias’s voyage was a significant milestone in the history of exploration. It opened up new possibilities for trade and exploration and paved the way for the eventual discovery of a sea route to India.
Impact and Legacy
Bartolomeu Dias’ voyage marked a pivotal turning point in European exploration and global history. His discoveries paved the way for future expeditions, reshaped the world map, and had lasting consequences on global trade and commerce.
Dias’ discovery of the Cape of Good Hope opened a direct sea route to the Indian Ocean, bypassing the dangerous and time-consuming land routes through the Middle East. This discovery revolutionized European trade with Asia, as it allowed for faster and more efficient transport of goods.
Spices, silks, and other valuable commodities could now be obtained directly from their source, leading to a surge in European wealth and influence.
Subsequent Expeditions, Map of bartolomeu dias voyage
Dias’ voyage inspired subsequent expeditions by Portuguese explorers, including Vasco da Gama, who successfully reached India in 1498. These expeditions continued to build on Dias’ discoveries, further expanding European knowledge of the world and establishing trade routes with the East.
Legacy on Global Geography and History
Dias’ discoveries had a profound impact on global geography and history. The Cape of Good Hope became a strategic waypoint for ships traveling between Europe and Asia, and it played a crucial role in the establishment of European colonies in the East.
The opening of the sea route to India also contributed to the rise of European colonialism and the global power dynamics that shaped the modern world.
Comparison to Other Maps
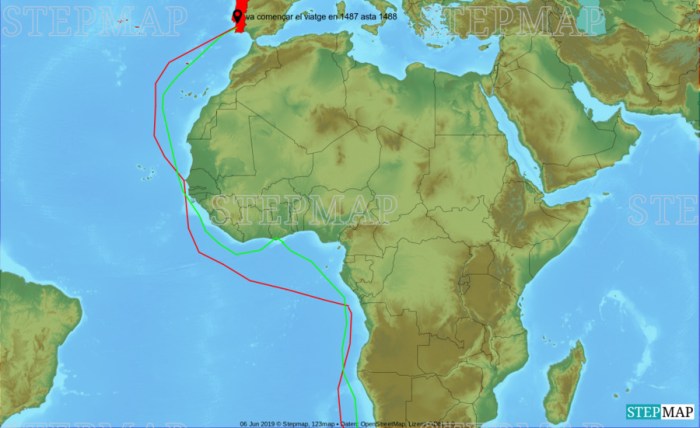
The map of Dias’ voyage can be compared to other contemporary maps of the period to understand the evolution of cartography and navigation techniques. These maps, such as the Fra Mauro map (1459) and the Cantino planisphere (1502), provide insights into the geographical knowledge and understanding of the time.
Similarities between these maps include their use of traditional symbols and iconography, such as wind roses, sea monsters, and depictions of ships. They also shared a general orientation, with north at the top and south at the bottom. However, there were also notable differences.
Accuracy and Detail
The map of Dias’ voyage was relatively accurate in its depiction of the African coastline, reflecting the increased knowledge gained from his expedition. In contrast, other contemporary maps often contained inaccuracies and distortions, particularly in areas that had not been extensively explored.
Projection and Scale
The map of Dias’ voyage used a cylindrical projection, which resulted in distortions in the representation of distances and shapes, especially near the poles. Other maps, such as the Cantino planisphere, employed more sophisticated projections, such as the Mercator projection, which provided a more accurate representation of the Earth’s surface.
Influence of Ptolemy
Many contemporary maps were influenced by the work of the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy. His theories and ideas, such as the concept of a spherical Earth, were reflected in the maps of the period. However, Dias’ voyage and other explorations challenged some of Ptolemy’s assumptions, leading to a gradual shift in cartographic practices.
FAQ Overview
What was the primary objective of Dias’ voyage?
To find a sea route to India around the southern tip of Africa.
What were some of the challenges Dias faced during his voyage?
Storms, strong currents, and unfamiliar coastlines.
What was the most significant discovery made by Dias?
The Cape of Good Hope, the southernmost point of Africa.